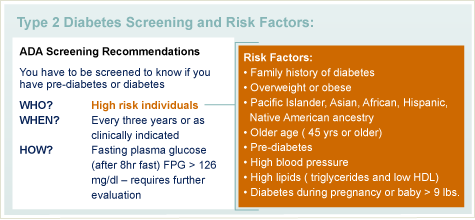
Risk Factors
Your risk of type 2 diabetes typically increases when you are:
- Older
- Less active
- Overweight or obese
Other risk factors are:
- Family history of diabetes in close relatives
- Being of African, Asian, Native American, Latino, or Pacific Islander ancestry
- High blood pressure
- High blood levels of fats, known as triglycerides, coupled with low levels of high-density lipoprotein, known as HDL, in the blood stream
- Prior diagnosis of pre-diabetes such as glucose intolerance or elevated blood sugar
- In women, a history of giving birth to large babies (over 9 lbs) and/or diabetes during pregnancy
Type 2 diabetes is strongly inherited
These are some of the statistics:
- 80-90% of people with Type 2 diabetes have other family members with diabetes.
- 10-15% of children of a diabetic parent will develop diabetes.
- If one identical twin has type 2 diabetes, there is up to a 75% chance that the other will also be diabetic.
- There are many genetic or molecular causes of type 2 diabetes, all of which result in a high blood sugar.
- As yet, there is no single genetic test to determine who is at risk for type 2 diabetes.
- To develop type 2 diabetes, you must be born with the genetic traits for diabetes.
- Because there is a wide range of genetic causes, there is also a wide range in how you will respond to treatment. You may be easily treated with just a change in diet or you may need multiple types of medication.
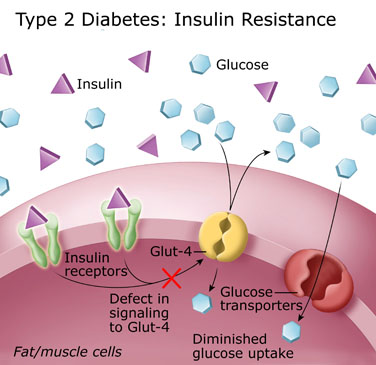
The hallmark of type 2 diabetes is resistance to the action of insulin and insufficient insulin to overcome that resistance
Insulin resistance and insufficient insulin production
Insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes means the signal insulin gives to a cell is weakened. This results in less glucose uptake by muscle and fat cells and a reduction in insulin mediated activities inside cells. Compounding this problem of resistance, there is additional defect in insulin production and secretion by the insulin producing cells, the beta cells in the pancreas.
As a group, everyone with with type 2 diabetes has both insulin resistance and an inability to overcome the resistance by secreting more insulin. But any given individual with type 2 may have more resistance than insulin insufficiency or the opposite, more insulin insufficiency than resistance. And the problems may be mild or severe. It is believed that the wide range of clinical presentation is because there are many, many genetic causes – and combinations of genetic causes – of type 2 diabetes. At present there is no single genetic test for type 2 diabetes. The diagnosis is made on the basis of the individual having clinical features consistent with type 2 diabetes, and by excluding other forms of diabetes.
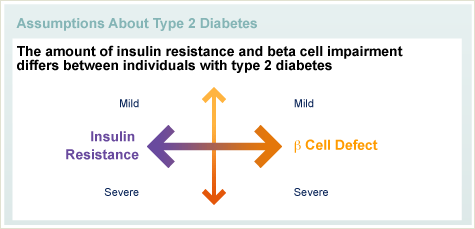

The progression from having a genetic predisposition to type 2 diabetes and the development of an elevated blood sugar or overt diabetes is affected by environmental factors
Development of type 2 diabetes
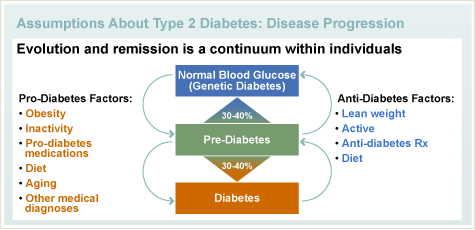
The development of type 2 diabetes is thought to be a progression from normal blood sugars to pre-diabetes to a diagnosis of overt diabetes. These stages are defined by blood sugar levels.
The timeline to developing an elevated blood sugar depends on many environmental factors (such as being overweight, physical activity, age, diet, illness, pregnancy, and medication) and also on how strong the gene traits are for diabetes. Ultimately, pre-diabetes and diabetes occur when the pancreas cannot make enough insulin to overcome the insulin resistance. Historically pre-diabetes and type 2 diabetes has been diagnosed when individuals are older; however, because of a wide-spread epidemic of obesity which causes insulin resistance, the diagnosis of type 2 diabetes is occurring more frequently at younger and younger ages.
People born with the genetic traits for diabetes are considered to be pre-disposed. Genetically predisposed people may have normal blood sugar levels, but many will have other markers of insulin resistance such, as elevated triglycerides and hypertension. When environmental factors are introduced, such as weight gain, lack of physical activity, or pregnancy, they are likely to develop diabetes.
Some individuals with other types of diabetes may be misdiagnosed as having type 2 diabetes. Up to 10% of individuals who are initially diagnosed with type 2 diabetes may actually have an adult onset of type 1 diabetes also known as LADA or Latent Autoimmune Diabetes of Adults.
Pre-diabetes
Pre-diabetes is a stage between not having diabetes and having type 2 diabetes. You have pre-diabetes when your blood sugars are above normal, but not so high as to meet the diagnostic criteria for type 2 diabetes. One in three people with pre-diabetes will go on to develop type 2 diabetes; however, with the correct lifestyle changes, including exercise, weight loss, a healthy diet, and the correct medications, the odds decrease so that only one in nine pre-diabetic people develop type 2 diabetes. In some cases, your blood sugar levels can return to normal. However, even if blood sugar levels return to normal, the genetic risk for type 2 diabetes remains unchanged – you must continue positive lifestyle changes, and medication or risk the return of elevated blood sugar levels.
Is Type 2 diabetes increasing?
Type 2 diabetes is increasing at an epidemic rate, and is being diagnosed at younger and younger ages. The most likely reason for this increase is that individuals with a genetic susceptibility to type 2 diabetes are developing the disease due to lifestyle changes – namely less physical activity, weight gain, and longer life span.
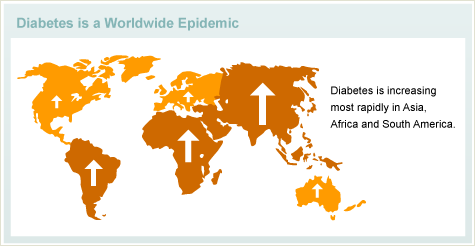
The good news is that scientific research confirms that by eating healthy foods, exercising regularly and maintaining an ideal body weight, you can delay or prevent the onset of type 2 diabetes.
Other conditions associated with type 2 diabetes
The insulin resistance syndrome
Individuals with type 2 diabetes are more likely to be diagnosed with other medical problems such as atherosclerosis, coronary artery disease, hypertension, obesity and dyslipidemia. Insulin resistance is thought to worsen and possibly directly cause these problems. The optimal medical care of type 2 diabetes includes not only controlling the blood glucose but also treating high blood pressure, high cholesterol or triglycerides, reducing excess weight and staying physically fit.
Self-assessment Quiz
Self assessment quizzes are available for topics covered in this website. To find out how much you have learned about Facts about Diabetes, take our self assessment quiz when you have completed this section. The quiz is multiple choice. Please choose the single best answer to each question. At the end of the quiz, your score will display. If your score is over 70% correct, you are doing very well. If your score is less than 70%, you can return to this section and review the information.

